Chapter 6: 3D Work and Concept
3D design has revolutionized the field of interior design, allowing clients and designers to visualize spaces before they are physically built. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, 3D renderings bring designs to life with realistic textures, lighting, and proportions, making it easier to communicate ideas and ensure alignment between the designer’s vision and the client’s expectations.
This chapter explores the significance of 3D design, its tools, processes, and the role it plays in modern interior design.
Introduction to 3D Design and Its Need
3D design has become an indispensable part of interior design due to its ability to create lifelike representations of spaces. It eliminates ambiguity by offering a detailed preview of how the final space will look, from the placement of furniture to the interplay of lighting and materials.
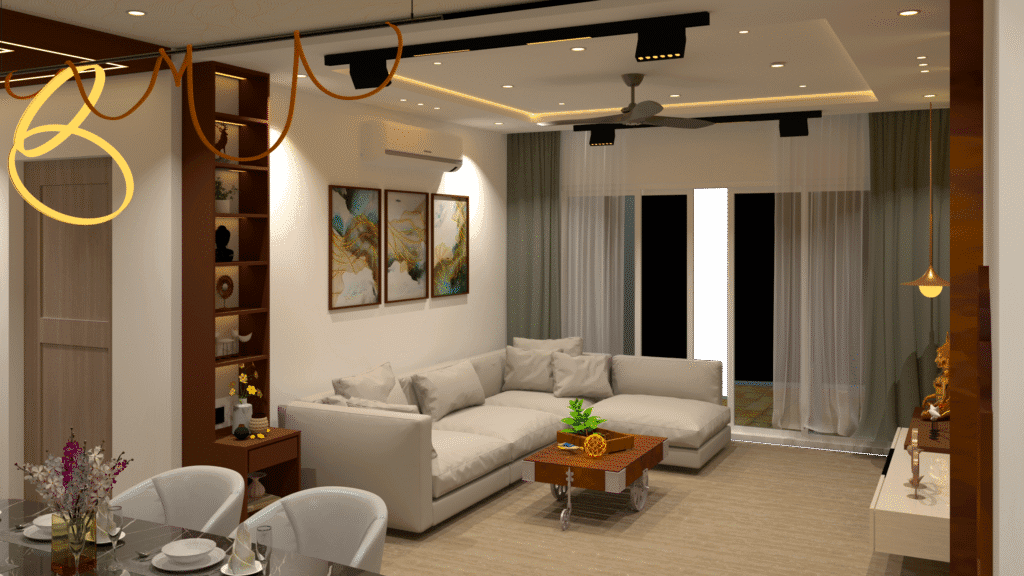

This technology not only helps clients visualize the design concept but also allows designers to test various ideas, ensuring that the end result is both functional and aesthetically pleasing. The ability to “walk through” a virtual space builds client confidence and minimizes revisions during construction.
The Role of 3D Concept Development
3D concept development bridges the gap between abstract ideas and practical execution. It transforms sketches, mood boards, and material selections into a tangible visual model. Designers use 3D models to experiment with layouts, color schemes, and textures, making adjustments in real-time based on feedback.
This process ensures that the final design is cohesive and aligned with the project’s goals. Additionally, 3D designs are a valuable tool for communicating with contractors and suppliers, providing precise details for construction and material sourcing.
Tools and Software for 3D Interior Design
A wide range of software tools is available for creating 3D designs, each offering unique features for different design needs. Popular options include:
AutoCAD: A powerful tool for precise technical drawings and 3D renderings.
SketchUp: Known for its user-friendly interface and versatility in creating detailed 3D models.
3ds Max: Offers advanced rendering capabilities with realistic lighting and textures.
Revit: Ideal for large-scale projects, integrating architectural and interior design elements.
Blender: A free, open-source tool with robust 3D modeling and animation features.
These tools allow designers to create detailed and realistic models, making the design process more efficient and effective.
Steps and Process to Create 3D Designs
The process of creating 3D designs involves several key steps:
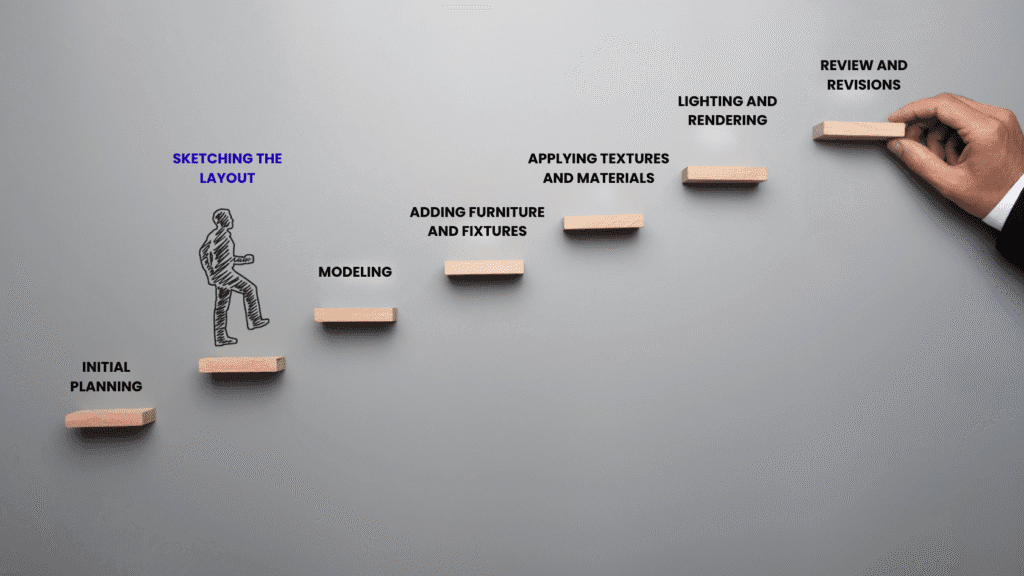
- Initial Planning: Understanding the client’s requirements, space dimensions, and design goals.
- Sketching the Layout: Creating a basic floor plan or layout as a foundation for the 3D model.
- Modeling: Building the 3D structure of the space, including walls, floors, ceilings, and partitions.
- Adding Furniture and Fixtures: Incorporating furniture, lighting, and decor elements into the model.
- Applying Textures and Materials: Selecting and applying materials to surfaces for a realistic look.
- Lighting and Rendering: Adding lighting effects to simulate natural and artificial illumination, followed by rendering to produce photorealistic images.
- Review and Revisions: Sharing the 3D model with the client for feedback and making necessary adjustments.
Realistic Textures
Realistic textures are crucial for creating lifelike 3D designs. High-quality texture mapping replicates the look and feel of materials such as wood, marble, fabric, and metal. By simulating the natural properties of these materials, designers can provide an accurate representation of how the finished space will appear.
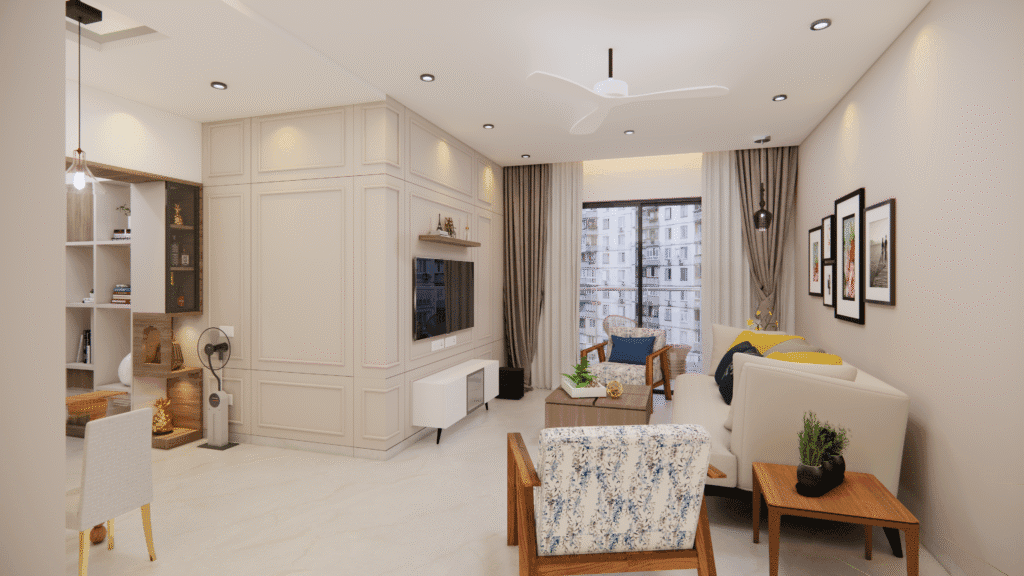

Tools like PBR (Physically Based Rendering) materials enhance realism by accurately reflecting light and shadows on surfaces.
Importance of Scale and Proportion
Maintaining accurate scale and proportion is fundamental in 3D design to ensure the functionality and visual harmony of a space. Incorrect proportions can make a room feel cramped or unbalanced.
Designers must account for the dimensions of furniture, room sizes, and pathways to create a layout that is both practical and aesthetically pleasing. 3D tools allow precise measurements, ensuring that every element fits perfectly within the space.
Customization and Client Collaboration in 3D
One of the biggest advantages of 3D design is its ability to support customization. Designers can create multiple iterations of a space, showcasing different layouts, color schemes, and material combinations.
Clients can provide input during this process, making real-time changes to the design. This collaborative approach enhances client satisfaction, as they feel actively involved in shaping the final outcome.
Common Challenges in 3D Design
Despite its advantages, 3D design comes with its challenges.
- Time-Consuming: Creating detailed 3D models and renderings can be time-intensive.
- High Costs: Advanced software and rendering tools require significant investment.
- Learning Curve: Mastering 3D design tools often demands technical expertise and training.
- Unrealistic Expectations: Clients may develop unrealistic expectations based on overly polished renderings that may differ slightly from real-world outcomes.
Addressing these challenges requires clear communication, efficient workflows, and realistic timelines.
Virtual Reality (VR) in Interior Design
Virtual Reality (VR) is an emerging technology that takes 3D design to the next level. With VR, clients can immerse themselves in a virtual representation of their space, walking through rooms and experiencing the design as if it were already built.
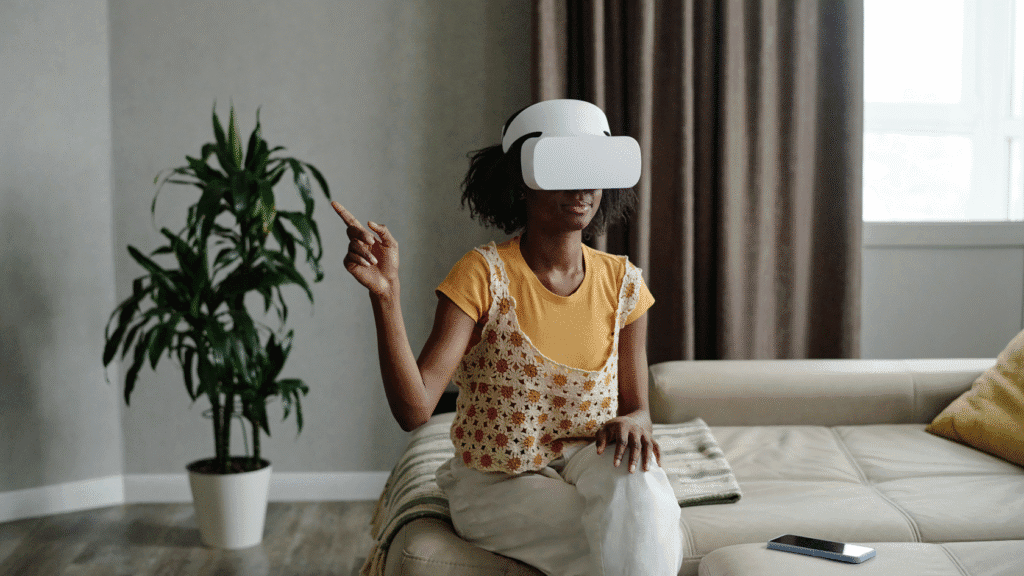

This interactive experience enhances decision-making by allowing clients to explore the layout, test furniture placement, and even feel the ambiance of different lighting setups. VR is particularly useful for large-scale projects, providing a dynamic and engaging way to finalize designs.
3D design has become an essential element in interior design, allowing designers to create realistic visualizations of spaces that bridge the gap between imagination and execution. Unlike traditional 2D plans, 3D renderings provide lifelike representations,showcasing textures, lighting, and scale.
This enhances communication between designers and clients, minimizes ambiguities, and allows real-time iterations, building confidence in the proposed design.
Key Points:
- Provides a preview of spatial arrangements, materials, and lighting before execution.
- Enhances client satisfaction by offering realistic visualizations.
- Helps in identifying design flaws and testing ideas during the conceptual stage.
Role of 3D Concept Development
3D concept development transforms abstract ideas into concrete visual models. Designers use 3D tools to experiment with layouts, color schemes, and textures, ensuring cohesiveness in the final output. It also facilitates collaboration with contractors and suppliers by providing precise technical details.
Key Points:
- Bridges the gap between sketches and execution.
- Enables real-time design adjustments based on feedback.
- Improves communication across teams by offering detailed visual references.
Tools and Software for 3D Interior Design
Interior designers have access to a range of tools for creating 3D designs, each tailored for specific needs:
- AutoCAD: Offers precision in technical 2D drawings.
- SketchUp: Easy to learn, great for creating quick 3D models.
- 3ds Max: Ideal for photorealistic rendering with advanced lighting and texturing.
- Revit: Combines architectural and interior design elements for large-scale projects.
- Blender: A free, open-source option with strong modelling and rendering capabilities.
Steps and Process to Create 3D Designs
Creating a 3D design involves systematic steps to ensure functionality and aesthetic appeal:
- Initial Planning: Understand client needs, goals, and space dimensions.
- Sketching the Layout: Draft a 2D floor plan as the foundation.
- Modelling: Develop the 3D structure, including walls, partitions, and other architectural features.
- Adding Furniture and Fixtures: Incorporate elements to match the functional and aesthetic goals.
- Applying Textures and Materials: Simulate real- world textures such as wood, fabric, and marble.
- Lighting and Rendering: Create natural and artificial lighting effects to enhance realism.
- Review and Revisions: Present the render to the client for feedback and adjustments.
Realistic Textures
Textures bring a 3D model to life, replicating surfaces like wood, stone, or metal. Modern tools use Physically Based Rendering (PBR) to ensure materials react realistically to light, providing depth and detail. High- quality textures make the final visualization more compelling and believable.
Key Points:
- Simulates real-world materials for authenticity.
- Enhances the realism of design through proper light reflection and shadowing.
Importance of Scale and Proportion
Proper scale and proportion are critical to the functionality and aesthetics of a space. Inaccurate proportions can lead to design failures, such as overcrowded layouts or impractical pathways. 3D tools ensure every element fits precisely within the intended space.
Key Points:
- Ensures balance and harmony in design.
- Creates practical layouts with accurate furniture and pathway dimensions.
Customization and Client Collaboration in 3D
Customization in 3D design allows clients to visualize multiple design options, including layouts, material combinations, and colour schemes. Real-time collaboration fosters better communication, enabling clients to actively shape the design process.
Key Points:
- Enhances client involvement with real-time modifications.
- Builds trust by offering multiple design iterations.
Common Challenges in 3D Design
While 3D design offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges:
- Time-Consuming: Creating detailed 3D models requires extensive time.
- Costly Software: Advanced tools and rendering software demand significant investment.
- Learning Curve: Mastering 3D tools requires technical expertise.
- Client Expectations: Overly polished visuals may lead to unrealistic expectations.
Virtual Reality (VR) in Interior Design
Virtual Reality (VR) takes 3D design a step further, allowing clients to immerse themselves in a virtual representation of their space.
VR creates an interactive experience, enabling clients to “walk through” a space and make decisions on layouts, materials, and lighting.
Key Points:
- Provides an immersive and interactive design review experience.
- Helps in finalizing large-scale projects with confidence.
- Allows real-time testing of design elements like furniture placement and ambiance.
Read Chapter – 7
Gantt Charts in Interior Design | A Popular Project Management Tool
A popular project management tool in interior design for visualizing and monitoring a project’s activities, timetable… Read More


